How to choose a gas shield
Laser cutting knowledge you must know

First of all, do you really know the function of gas shield?
- Use the gas shield to blow away the slag in the coaxial kerf
- Cool the surface of the processed object to reduce the heat affected zone
- Cool the protective lens to avoid contaminating and overheating.
- Some cutting gases can also protect the base metal.
- Gas pressure and type has great influence on the cutting process.
- Gas shield type will affect the cutting performance, including cutting speed and cutting quality.
Gas shield types and characteristics
The most commomly used in laser cutting are oxygen, nitrogen and air.
 左右滑動看表格
左右滑動看表格| Gas | Strengths | Weakness |
| Oxygen |
|
Combustion gas, easy to burn and return to slag |
| Nitrogen |
|
Expensive,High purity demand and large usage in cutting process |
| Air |
|
Can also help combustion, lower degree than oxygen to burn and return to slag (Not recommended when product cutting is demanding) |
The suitable cutting materials for gas shield
Since the gas shields have each corresponding characteristics, the suitable cutting materials for each gas are also different.
 左右滑動看表格
左右滑動看表格| Gas | Suitable material for cutting |
| Oxygen | Carbon steel, high tension plate, tool plate, stainless steel, electroplated steel, copper, copper alloy, etc. |
| Nitrogen | Stainless steel, electroplated steel, brass, copper, aluminum, aluminum alloy, etc. |
| Air | Carbon steel, aluminum, stainless copper, brass, electroplated steel, non-metal sort, etc. |
Gas shield purity standard
Different materials in laser process need corresponding gases. Impurities in the gas shield will damage the lens leading to fluctuations in cutting power and section inconsistency.
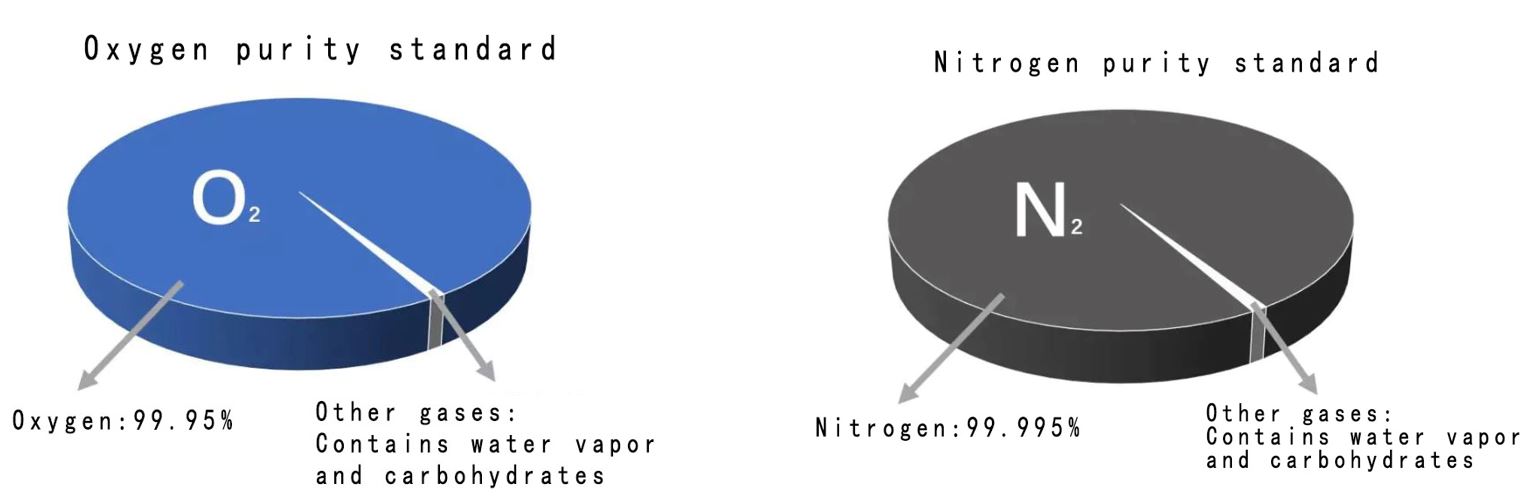
 左右滑動看表格
左右滑動看表格| Gas | Purity | water vapor Maximum content |
Hydrocarbon Maximum content |
| Oxygen | 99.95% | <5 ppm | <1 ppm |
| Nitrogen | 99.995% | <5 ppm | <1 ppm |
Gas shield pressure standard
Each gas shield can use different air pressure. As a matter of experience, usually base on the folloing form.
 左右滑動看表格
左右滑動看表格| Gas | Oxygen | Air | Nitrogen |
| Maximum pressure value | <1 Mpa | 1.8 Mpa | 2 Mpa |
The gas shield can prevent slag during the cutting process, thereby protecting the lens inside the laser head.In other words, in the case of same process power, the material and the thickness sheet, the larger gas pressure, the more soot that can be blown off at the unit speed.Therefore, the higher air pressure, the faster speed laser can cut.
According to the above inference, we can draw some conclusions that thick plate cutting speed:
Oxygen < Air < Nitrogen
Notice:
The above general rules are not applicable when cutting thick plate.It's necessary to choose the type of cutting gases basing on the individual characteristics.I believe that you had preliminarliy understand the characteristics of three gas shields.Let's take a closer look.
I believe that you had preliminarliy understand the characteristics of three gas shields.
Let's take a closer look.
Oxygen
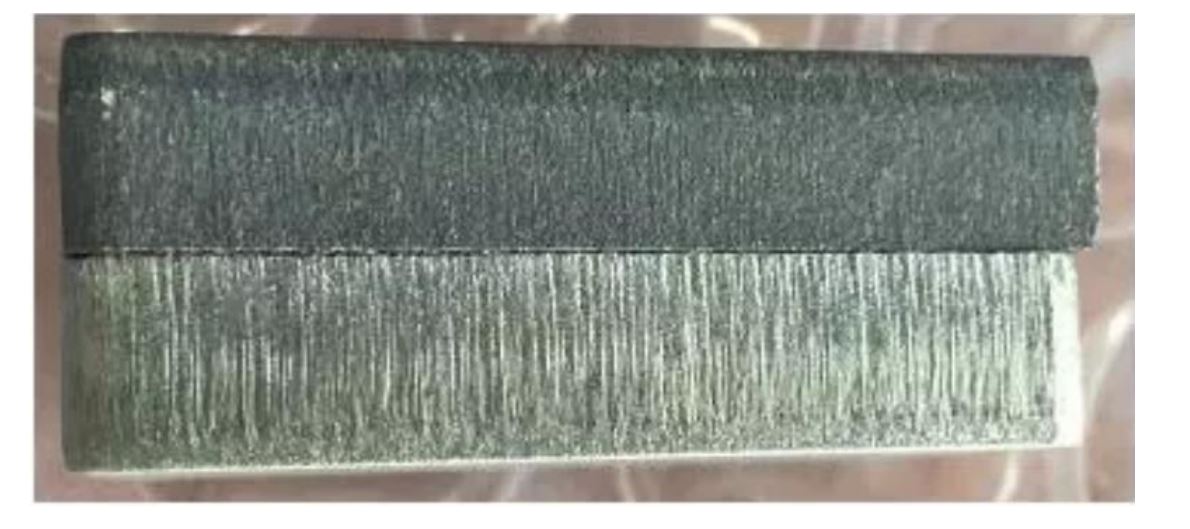
- Increasing cutting power by making used of oxygen reaction heat,oxidized film will increase beam spectral absorption factor and section is inrescence and yellow.
- Mainly used for rolling steel, rolled steel for welding structure, carbon steel for mechanical construction, high tension plate, tool plate, stainless steel, plated steel, copper, copper alloy, etc.
- The rate of purity requirement is generally 99.95% or higher. The main functions are helping burn and blow off the cut melt. The pressure and flow rate are different, which is inseparable from the size of the nozzle model and the thickness of the cutting material.

Nitrogen
- Using oxygen may form oxide film whrn cutting metals, Nitrogen can be used for oxyation-free cutting to prevent oxide film. Therefore, there were features that can directly welded, smeared, and high corrosion resistance. The slit is whitish.
- Mainly used for stainless steel, eletroplated steel, brass, aluminum alloy. its role is to prevent oxidation reactiions and blow off melt.
- High purity requirements for nitrogen (especially 8mm or more stainless steel, generally required to reach 99.999% purity), pressure requirements are relatively large, generally about 1.5Mpa, if you want to cut more than 12mm, or thicker 25mm stainless steel requires pressure to 2Mpa or higher. The flow rate will be influenced according to the type of nozzle, and vary within wide limits, for example, cutting 12mm stainless steel requires 150m3/h while cutting 3mm requires only 50m3/h.
Air
- Air can be supplied directly from the air compressor, so it's relatively cheaper than other gases. Although there is 20% oxygen in the air, the cutting efficiency is far behind the oxygen, and the cutting ability is nearly the nitrogen. A trace oxide film appears on the cutting surface, but it can be used as a precautionary measure to prevent coating layer from falling off. The slit is yellow.
- The main materials are aluminum, stainless copper, brass, plated steel, non-metal, etc.
- However, when the cutting product is demanding, aluminum, aluminum alloy or stainless steel are not suitable because air will oxidize the base material.
As mentioned above, many gases can be used in general, the focal point is to consider costs and product requirements.