How to determine the focus position?

When operate laser cutting process, different focus position presence different cutting quality. Thus, in order to improve laser cutting quality, the adjustment of focus position is very important.
There're always some problems confused you in the operation.
- Why is there always adhering slag when cutting?
- The cutting surface of plate is always rough?
- How to determine the focus position?

Before these, we should first understand the importance of the focus.
When cutting high quality or thicker workpieces, some key technologies need to be controlled and solved.Focus position technology is one of them.The main advantage of laser cutting is high power density. Thus, the smaller focus speckle is, the narrower slit will be produced. Because the depth of focus is shallow, the focus speckle is small. The depth of focus is related to lens’ diameter and the material for a high-quality cutting.Therefore, focus correction is relatively important to the cutting surface.When focus position is the most appropriate, the slit is small and cutting quality is highest which can obtain the best cutting efficiency. Different focus position corresponds different cutting rough extent, laser cutting quality is determined by the relative position of focus and cutting plate to a large extent.
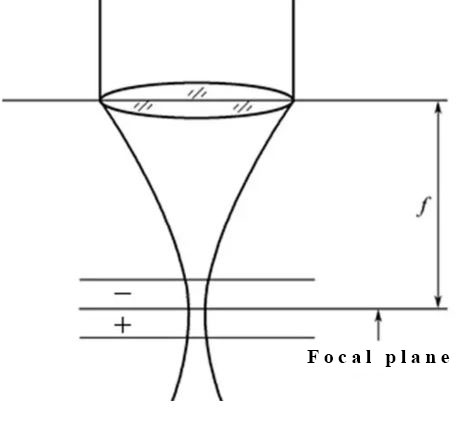
Focus position
Focus position is the relative position of focus and workpiece surface in theory, take the workpiece surface as standard, positive above the workpiece surface, negative under the workpiece surface.
 左右滑動看表格
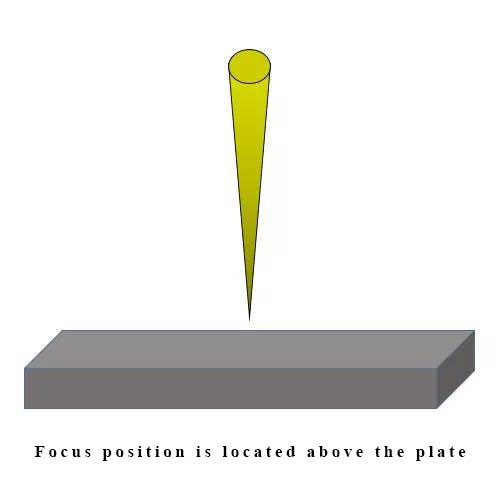
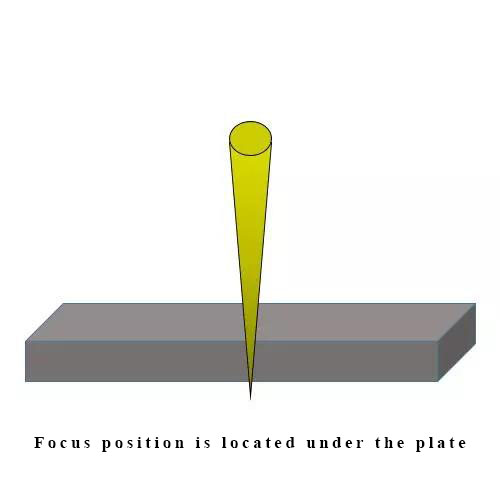
左右滑動看表格| Name | Focus position | Features | Material |
| Positive focus | Focus position is located above the plate | Focus is away from cutting surface, cut width is relatively bigger than focus on the workpiece. In this situation, the airflow needs to be small, and the temperature need to enough, so the cutting time is quite long. |
Frequently used in cutting molten metal. |
| Negative focus | Focus position is located under the plate | Focus position is located under the surface. This cutting method is mainly used for cutting high hardness material. The reason why the focus position under the surface is that the plate needs a big cut width. Otherwise, the gas shield inject from nozzle is not enough leading to unblown slag. The disadvantage is that cutting surface is quite rough and inappropriate to be used in high precision cutting. |
Frequently used in cutting stainless steel. |
| 0 focus | Focus position is located on the plate. | In this cutting method, the workpiece upper and lower surface smoothness are different. The surface close to the focus is smooth while the lower surface away from the focus is rough. | Commonly used in cutting SPC, SPH, SS41. |
Influnce of cutting quality
When the thickness, material and quality of workpiece are different, focus position are different as well.
Take stainless steel as example:
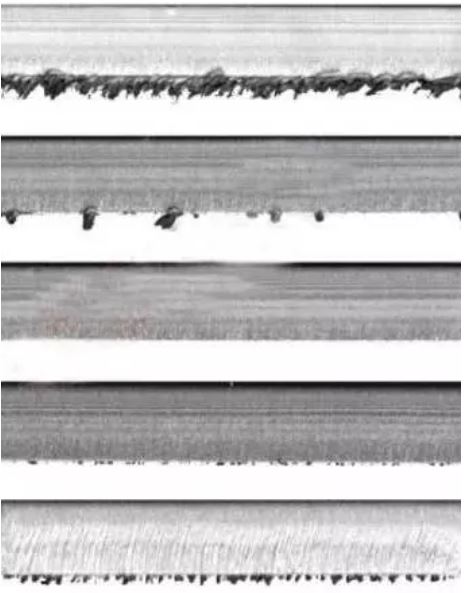
1.
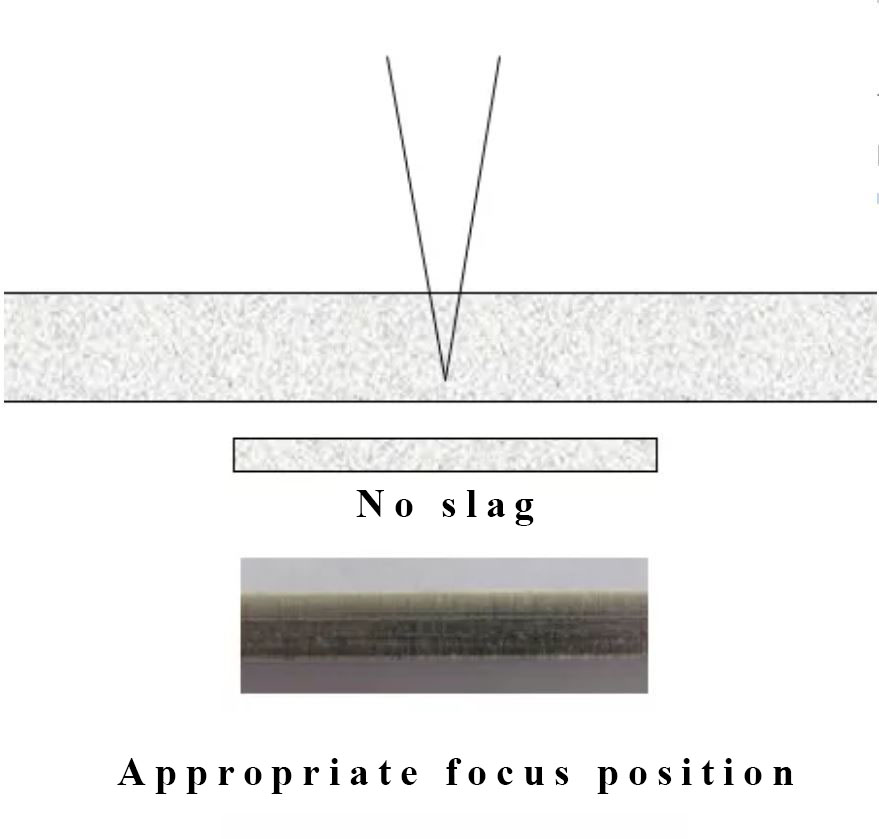
The average energy of workpiece bottom unit area is increased, the material that being cut and cut edge are melted and liquid flow state, in this time, gas shield pressure and cutting speed are constant, the melted material is englobement and cohere to the lower surface.
2.
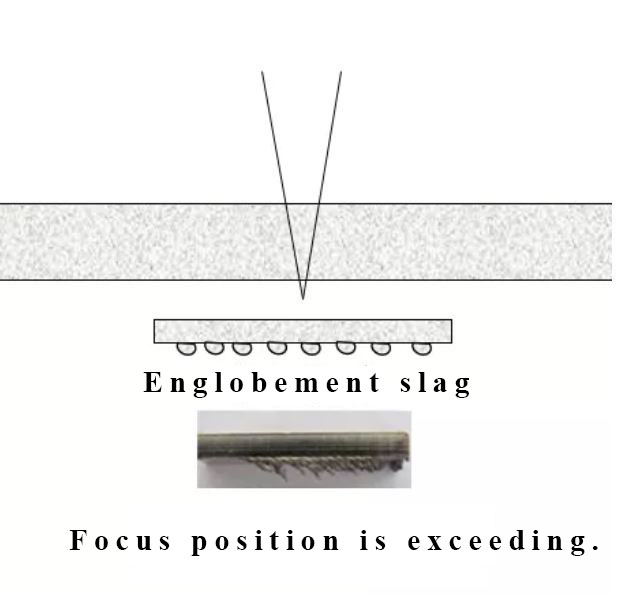
The material that being cut is melted while the cut edge hasn’t melted yet and slag is blown away, finally formed a no-slag slit.
3.
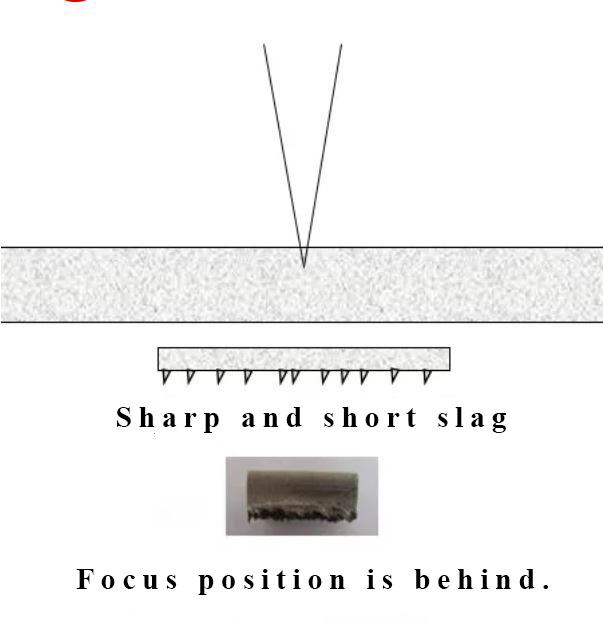
The average energy of workpiece bottom unit area is reduced, cutting power is weak so the material cannot be melted completely and blown away by gas shield, resulting in uncompleted material cohere to the blow surface and present a sharp and short tip slag.
In the actual production, focus position located on or below the surface are demanded for cutting stainless steel, because the upper slit width is expanded, and gas shield and slag fluidity are high, the smooth surface range is expanded, and quality is increased.
Determine the focus position
There are 5 ways to determine focus position in the industry production.
CNC positioning control, bevel focus burning, the blue spark, collimating and retrofit individual moving lens.
 左右滑動看表格
左右滑動看表格| Method | Operation |
| CNC positioning control | Make a cutting head focus motion from the top to bottom, marking on the plate. Marking diameter is zero focus(reference focus) |
| Bevel focus burning | Use a beveled plastic plate and move it horizontally, the smallest laser beam is the focus. |
| Blue spark | Remove nozzle, blowing cutting gas directly, injecting pulsed laser on stainless steel, make a cutting head motion from the top to bottom until blue spark which is the focus. |
| Collimating | It’s the most common way that using collimating on the laser output, laser beam diameter becomes bigger and divergence angle becomes smaller after collimating, laser beam size become identical before the proximal and remote focus in cutting area. |
| Retrofit individual moving lens | Retrofit individual moving lens, it’s a separated part with z axis which control the distance from nozzle to the surface. When the machine table or optical axis moving, F axis from proximal to remote is also moving which can make the speckle diameter be consistent in process area after laser beam focused. |
Remark
Because laser power density is related to cutting speed, the choice of lens focal length is an issue. When laser beam focused, the speckle size is proportional to lens focal length. When laser beam focused through short focal length, the speckle size is small and power density in focus area is very high which benefits for fast cutting. However, the depth of focus is short and adjustable margin is small, commonly used in thin object fast cutting. Long focal length has wider depth of focus, as long as it has a sufficient power density it can afford thick object.
We had understood the preliminary focus position.Let's learn more now.
Influence of incision width, slop, roughness cutting surface and slag
Laser cutting focus position is directly affect incision width, slop, level of rough cutting surface and slag. Different focus position cause different laser beam diameter and depth of focus of the processed surface.And also affect the shape of incision, flow of gas and molted metal in the incision.